Lesson 05: User-Defined Functions
Objectives
- Learn how to create and use your own MATLAB functions
- Learn how to create and use anonymous functions
Background
A user-defined function is a MATLAB program that is created by the user and saves as a function file. It can be used like a built-in function. A function usually has input arguments (or parameters) and/or output variables (or parameters). Both parameters can be scalars, vectors, matrices of any size. In MATLAB, a function can has any number of input and output parameters, also including zero.
5.1 Create a Function Files
Both scripts and function files allow you to reuse sequences of commands by storing them in program files. Script files are the simplest type of program, since they store commands exactly as you would type them at the command line. Function files provide more flexibility, primarily because you can pass input values and return output values. For example, this function named fact computes the factorial of a number (n) and returns the result (f).
function f = fact(n)
f = prod(1:n);
end
A function must be define within a file, not at the command line, and the function is usually stored in its own file. When creating a function file, the filename must be the same as the function name, since MATLAB associates the program with the filename. You can save the file either in the current project folder, or in a folder on the MATLABN search path.
You can call the function from the command line, using the same syntax rules that apply to MATLAB built-in functions. For instance, calculate the factorial of 5:
>> x = 5;
>> y = fact(5)
y = 120
To create a function file, you can click  icon, then select
icon, then select ![]() icon to create a function.
icon to create a function.
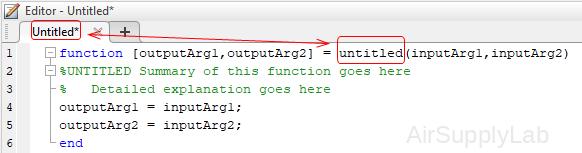
function [outputArg1,outputArg2] = untitled(inputArg1,inputArg2)
%UNTITLED Summary of this function goes here
% Detailed explanation goes here
outputArg1 = inputArg1;
outputArg2 = inputArg2;
end
- untitled: (required) the name of the user-defined function
Valid function names follow the same rules as variable names. They must start with a letter, and can contain letters, digits, or underscores. - inputArg1, inputArg2: (optional) input parameters
- outoutArg1, outputArg2: (optional) output parameters
The parentheses are needed even if the function has no input parameter.
To avoid confusion, use the same name for both the function file and the first function within the file. MATLAB associates your program with the file name, not the function name.
Comments in Functions
Function with One Output
Function with One Output
If your function returns one output, you can specify the output name after the function keyword.
function myOutput = myFunction(x)
Example
Define a function in a file named average.m that accepts an input vector, calculates the average of the values, and returns a single result.
function ave = average(x)
ave = sum(x(:))/numel(x);
end
Call the function from the command line.
>> z = 1:99;
>> ave = average(z)
ave = 50
Function with Multiple Inputs
Function with Multiple Inputs
If your function accepts any inputs, enclose their names in parentheses after the function name. Separate inputs with commas.
function y = myFunction(one,two,three)
Example
Define a function to multiply x and y together.
function output = g(x,y)
a = x .* y;
output = a;
end
Call the function from the command line.
>> x = 1:5; y = 5:9;
>> g(x,y)
ans = 5 12 21 32 45
Function with Multiple Outputs
Function with Multiple Outputs
If your function returns more than one output, enclose the output names in square brackets.
function [one,two,three] = myFunction(x)
Example
Define a function in a file named stat.m that returns the mean and standard deviation of an input vector.
function [m,s] = stat(x)
n = length(x);
m = sum(x)/n;
s = sqrt(sum((x-m).^2/n));
end
Call the function from the command line.
>> values = [12.7, 45.4, 98.9, 26.6, 53.1];
>> [ave,stdev] = stat(values)
ave = 47.3400
stdev = 29.4124
Function with No Output and/or No Input
Function with No Output
If there is no output, you can omit it.
function myFunction(x)
Or you can use empty square brackets.
function [] = myFunction(x)
Function with No Output and No Input
If there is no output and no input, you can omit it.
function myFunction()
Or you can use empty square brackets.
function [] = myFunction()
Example
Define a function in a file named star.m that draw a star in polar coordinates.
function [] = star()
theta = pi/2:0.8*pi:4.8*pi;
r = ones(1,6);
polarplot(theta,r)
end
Call the function from the command line.
| >> star | 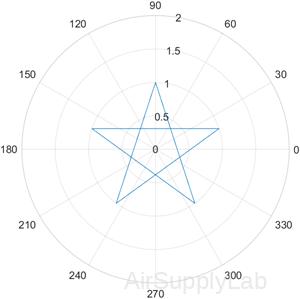 |
There are no returned values, but a figure window opens showing a star drawn in polar coordinates.
Multiple Functions in a Function File
Multiple Functions in a Function File
Define two functions in a file named stat2.m, where the first function calls the second.
function [m,s] = stat2(x)
n = length(x);
m = avg(x,n);
s = sqrt(sum((x-m).^2/n));
end
function m = avg(x,n)
m = sum(x)/n;
end
Function avg is a local function. Local functions are only available to other functions within the same file.
Call function stat2 from the command line.
>> values = [12.7, 45.4, 98.9, 26.6, 53.1];
>> [ave,stdev] = stat2(values)
ave = 47.3400
stdev = 29.4124
Function with Argument Validation
Function with Argument Validation
Define a function that restricts input to a numeric vector that contains no Inf or NaN elements. This function uses the arguments keyword, which is valid for MATLAB versions R2019b and later.
function [m,s] = stat3(x)
arguments
x (1,:) {mustBeNumeric, mustBeFinite}
end
n = length(x);
m = avg(x,n);
s = sqrt( sum((x-m).^2/n) );
end
function m = avg(x,n)
m = sum(x)/n;
end
In the arguments code block, (1,:) indicates that x must be a vector. The validation functions, {mustBeNumeric, mustBeFinite}, restrict the elements in x to numeric values that are not Inf or NaN. For more information, see Function Argument Validation.
Calling the function with a vector that contains an element that is NaN violates the input argument declaration. This violation results in an error being thrown by the mustBeFinite validation function.
>> values = [12.7, 45.4, 98.9, NaN, 53.1];
>> [ave,stdev] = stat3(values)
Invalid input argument at position 1. Value must be finite.
Practice Exercise 5.1
- Assuming that the matrix dimensions agree, create and test MATLAB functions to evaluate the following simple mathematical functions with multiple input vectors and a single output vector:
- \(z(a,b,c) = a{b^c}\)
- \(z(w,x,y) = w{e^{(x/y)}}\)
- \(z(p,t)={}^{p}\!\!\diagup\!\!{}_{\sin (t)}\;\)
- Assuming that the matrix dimensions agree, create and test MATLAB functions to evaluate the following simple mathematical functions with a single input vector and multiple output vectors:
- \(f(x)=\cos (x)\)
\(f(x)=\sin (x)\) - \(f(x)=5{{x}^{2}}+2\)
\(f(x)=\sqrt{5{{x}^{2}}+2}\) - \(f(x)=\exp (x)\)
\(f(x)=\ln (x)\)
- \(f(x)=\cos (x)\)
- Assuming that the matrix dimensions agree, create, and test MATLAB functions to evaluate the following simple mathematical functions with multiple input vectors and multiple output vectors:
- \(f(x,y)=x+y\)
\(f(x,y)=x-y\) - \(f(x,y)=y{{e}^{x}}\)
\(f(x,y)=x{{e}^{y}}\)
- \(f(x,y)=x+y\)
5.2 Anonymous Functions and Function Handles
Anonymous Functions and Function Handles
Anonymous functions are defined in the command window , in a script, or inside regular user-defined functions, and are variable. Anonymous functions have been introduced in MATLAB 7. They have several advantages over inline function. Right now both anonymous and inline functions can be used, but inline function will gradually be phased out.
An anonymous function is created by typing the following statement:
functionName = @ (var1, var2, ...) expression
- functionName is the name of the anonymous function.
- @ symbol alerts MATLAB this is a function.
- var1, var2, etc. are a comma separated list of arguments of the function.
- expression is a single mathematical expression involving those variables. The expression can include any built-in or user-defined functions.
The above command creates the anonymous function, and assigns a handle for the function to the variable name on the left of the = sign. Function handles provide means for using the function, and passing it to other functions.
Include Built-In Function
Include Built-In Function
The common logarithm, is the logarithm base 10. It is the inverse of the exponential function 10x. In Calculus and Precalculus classes, it is usually denoted log.
The natural logarithm, is the logarithm base e. It is the inverse of the exponential function ex. In Calculus and Precalculus classes, it is often denoted ln.
The log function in MATLAB is the natural logarithm, and there is no ln function in MATLAB. We can create an anonymous function to define ln function:
>> ln = @(x) log(x);
It can be used like any other function:
>> ln(10)
ans = 2.3026
Include Predefined Variables
Include Predefined Variables
The expression can include predefined variables that are already defined when the anonymous function is defined. For example, if three variables a, b, and c have been assigned values, then they can be used in the expression of the anonymous function:
>> a = 3; b = 4; c = 5;
>> parabola = @(x) ( a * x + b ) * x + c;
>> parabola(10)
ans = 345
It is important to note that MATLAB captures the values of the predefined variables when the anonymous function is defined. This means that if subsequently new values are assigned to the predefined variables, the anonymous function is not changed.So in the above example, the parabola is always defined so that the three coefficients, a, b, and c are given by 3, 4, and 5, respectively, even though the values of a,b, and c may be altered subsequently.The anonymous function has to be redefined in order for the new values of the predefined variables to be used in the expression.
Include User-Defined Function
Include User-Defined Function
It is possible to assign a function handle to any function.
Create a function file call distance.m.
function result = distance(t)
result = 1/2 * 9.8 * t .^ 2;
end
Assign the handle distance_handle to the distance function.
>> distance_handle = @(t) distance(t);
Multiple-Input Parameters
Multiple-Input Parameters
You can create anonymous functions having more than one input. For example, to define the function \(\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}\), type
>> sqrtsum = @(x,y) sqrt(x .^ 2 + y .^ 2);
>> sqrtsum(3, 4)
ans = 5
No-Input Parameters
No-Input Parameters
To construct a handle for an anonymous function that has no input parameters, use empty parentheses for the input parameter list, as shown by the following:
>> d = @() date;
Use empty parentheses when invoking the function, as follows
>> d()
ans = '15-Sep-2019'
Calling One Function within Another
Calling One Function within Another
One anonymous function can call another to implement function composition. Consider the function \(5\sin ({{x}^{3}})\). It is composed of the function \(g(x)=5\sin x\) and \(f(x)={{x}^{3}}\). In the following function whose handle is h calls the functions whose handles are f and g to compute \(5\sin ({{2}^{3}})\).
>> f = @(x) x .^ 3;
>> g = @(x) 5 * sin(x);
>> h = @(x) g(f(x));
>> h(2)
ans = 4.9468
Once the workspace is cleared, the anonymous function no longer exists. Anonymous function can be saved as .mat files, and it can be restored with load command.
Save Anonymous Functions
>> ln = @(x) log(x);
>> save my_ln_function ln
Load Anonymous Functions
>> load my_ln_function
Practice Exercise 5.2
- Write a program that creates three anonymous functions representing the functions \(f(x)=10\cos x\), \(g(x)=5\sin x\), and \(h(a,b)=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}\). Plot \(h\left( f(x),g(x) \right)\) over the range \(-10\le x\le 10\) .
- Create an anonymous function for \(10{{e}^{-2x}}\) and use it to plot the function over the range \(0\le x\le 2\).
5.3 Function Functions
Function Functions
MATLAB function functions evaluate mathematical expressions over a range of values. They are called function functions because they are functions that accept a function handle (a pointer to a function) as an input. Each of these functions expects that your objective function has a specific number of input variables. One example of a MATLAB build-in function functions is the function plot, fplot. This function requires two inputs:a function (or a function handle), and a range over which to plot.
Use of fplot with the function handle ln, define as:
>> ln = @(x) log(x);
The function handle can now be used as input to the fplot function:
>> fplot(ln, [0.1, 10])
Some of the more common MATLAB function functions are list as below table. Type help fun_name to learn how to use each of these functions.
| Function Name | Description |
|---|---|
| fminbnd | Minimize a function of one variable. |
| fminsearch | Minimuze function of several variables |
| fzero | Find a zero of a function of one variable. |
| quad | Numerically integrate a function. |
| quadl | Numerically evaluate integral, adaptive Lobatto quadrature. |
| dblquad | Numerically evaluate double integral. |
| ezplot | Easy to use function plotter. |
| fplot | Plot a function by name. |
Finding the Zero of a Function
You can use fzero function to find the zero of a function of a single variable.
| fzero(@function,x0) | Use the starting value x0 to find a zero of the single-variable function described by the handle @function. |
Where @function is a function handle and x0 is a user-supplied guess for the zero. The fzero function returns a value of x that is near x0.
Root Starting From One Point
Calculate π by finding the zero of the sine function near 3.
>> fun = @sin; % function
>> x0 = 3; % initial point
>> x = fzero(fun,x0)
x = 3.1416
Root Starting From an Interval
Find the zero of cosine between 1 and 2.
>> fun = @cos; % function
>> x0 = [1 2]; % initial interval
>> x = fzero(fun,x0)
x = 1.5708
Note that cos(1) and cos(2) differ in sign.
Root of a Function Defined by a File
Find a zero of the function \(f(x)={{x}^{3}}-2x-5\).
First, write a file called f.m.
function y = f(x)
y = x .^ 3 - 2 * x - 5;
end
Save f.m on your MATLAB path.
Find the zero of f(x) near 2.
>> fun = @f; % function
>> x0 = 2; % initial point
>> z = fzero(fun,x0)
z = 2.0946
Since f(x) is a polynomial, you can find the same real zero, and a complex conjugate pair of zeros, using the roots command.
>> roots([1 0 -2 -5])
ans =
2.0946
-1.0473 + 1.1359i
-1.0473 - 1.1359i
Minimizing a Function of One Variable
Minimizing a Function of One Variable
The fminbnd function finds the minimum of a function of a single variable, witch is denoted by x.
| fminbnd(@function,x1,x2) | Returns a value of x in the interval x1 ≤ x ≤ x2 that corresponds to a minimum of the single-variable function described by the handle @function. |
Where @function is a function handle. The fminbnd function returns a value of x that minimizes the function in the interval x1 ≤ x ≤ x2.
Minimum of sin
Find the point where the sin(x) function takes its minimum in the range \(0<x<2\pi \).
>> fun = @sin;
>> x1 = 0;
>> x2 = 2 * pi;
>> x = fminbnd(fun,x1,x2)
x = 4.7124
To display precision, this is the same as the correct value \(x={}^{3\pi }\!\!\diagup\!\!{}_{2}\;\).
>> 3 * pi / 2
ans = 4.7124
Minimize a Function Specified by a File
Minimize a function that is specified by a separate function file. A function accepts a point x and returns a real scalar representing the value of the objective function at x.
Write the following function as a file, and save the file as scalarobjective.m on your MATLAB path.
function f = scalarobjective(x)
f = 0;
for k = -10:10
f = f + (k+1)^2 * cos(k*x) * exp(-k^2 / 2);
end
Find the x that minimizes scalarobjective on the interval 1 ≤ x ≤ 3.
>> x = fminbnd(@scalarobjective, 1, 3)
x = 2.0061
Minimizing a Function of Several Variables
Minimizing a Function of Several Variables
To find the minimum of a function of more than one variable, use the fminsearch function.
| fminsearch(@function,x0) | Uses the starting vector x0 to find a minimum of the multivariable function described by the handle @function. |
Where @function is a function handle. The vector x0 is a guess that must be supplied by the user.
Minimize Rosenbrock's Function
Minimize Rosenbrock's function, a notoriously difficult optimization problem for many algorithms:
\(f(x)=100{{({{x}_{2}}-x_{1}^{2})}^{2}}+{{(1-{{x}_{1}})}^{2}}\)
The function is minimized at the point x = [1,1] with minimum value 0.
Set the start point to x0 = [-1.2, 1] and minimize Rosenbrock's function using fminsearch. The anonymous function shown here defines the function and returns a function handle called fun:
>> fun = @(x) 100*(x(2) - x(1)^2)^2 + (1 - x(1))^2;
Pass the function handle to fminsearch:
>> [x, fval] = fminsearch(fun,[-1.2, 1])
x = 1.0000 1.0000
fval = 8.1777e-010
This indicates that the minimizer was found to at least four decimal places with a value near zero.
Multiple Value Vector
Find the minimum of some function: \(f(x,y)={{(x-1)}^{2}}+{{(y-2)}^{2}}\) which has a discernible minimum at (1, 2); you could use:
>> [rval, fval] = fminsearch(@(r) (r(1)-1).^2+(r(2)-2).^2, [0 0])
rval = 1.0000 2.0000
fval = 1.8692e-09
to have MATLAB start at the origin and find the value of the vector r that has the x and y coordinate in it. Since this function only has one minimum, MATLAB should be able to find it as long as the initial guess is somewhat reasonable.
Practice Exercise 5.3
- Create an anonymous function for \(20{{x}^{2}}-200x+3\) and use it
- To plot the function to determine the approximate location of its minimum.
- With the fminbnd function to precisely determine the location of minimum.
5.4 Sub-, Nested and Private Functions
Subfunctions (Local Functions)
Subfunctions (Local Functions)
Subfunctions can be created by grouping functions together in a single file.There are two approaches:
- You can add subfunctions to a script.
- You can use multiple subfunctions in a primary function.
MATLAB program file can contain code for more than one function. In a function file, the first function in the file is called the primary function (or main functions). The primary function is visible to functions in other files, or you can call it from the command line. Additional functions within the files are called subfunctions (also called local functions). It can occur in any order after the primary function. Sunfunctions are only visible to other functions in the same file.
Each MATLAB function file has one primary function. The name of the M-file must be the same as the primary function name.
Example
Create a function file named mystates.m that contains a main function, mystates, and two subfunctions, mymean and mymedian.
function [avg, med] = mystats(x)
n = length(x);
avg = mymean(x,n);
med = mymedian(x,n);
end
function a = mymean(v,n)
% MYMEAN Example of a local function.
a = sum(v)/n;
end
function m = mymedian(v,n)
% MYMEDIAN Another example of a local function.
w = sort(v);
if rem(n,2) == 1
m = w((n + 1)/2);
else
m = (w(n/2) + w(n/2 + 1))/2;
end
end
The subfunction mymean and mymedian calculate the average and median of the input list. The primary function mystates determines the length of the list n and passes it to the subfunctions.
Nested Functions
Nested Functions
A nested function is a function that is completely contained within a parent function. Any function in a program file can include a nested function. You have to terminate a nested function with an end statement.
For example, this function named parent contains a nested function named nestedfx:
function parent
disp('This is the parent function')
nestedfx
function nestedfx
disp('This is the nested function')
end
end
The primary difference between nested functions and other types of functions is that they can access and modify variables that are defined in their parent functions. As a result:
- Nested functions can use variables that are not explicitly passed as input arguments.
- In a parent function, you can create a handle to a nested function that contains the data necessary to run the nested function.
Minimum Point on the Parabola
The following example constructs a function handle for a nested function p(x) and then passes the handle to the MATLAB function fminbnd to find the minimum point on the parabola.
The parabola function constructs and returns a function handle f for the nested function p that evaluates the parabola turns a function handle f for the nested function p that evaluates the parabola \(a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c\). This handle gets passed to fminbnd.
function f = parabola(a, b, c)
f = @p;
% Nested function
function y = p(x)
y = polyval( [a,b,c],x);
end
end
In the command window type:
>> f = parabola(4, -50, 5);
>> fminbnd(f, -10, 10)
ans = 6.2500
Note: The function p(x) can see the variables a, b, and c in the calling function's workspace.
Visibility of Nested Functions
Consider the following representation of some functions named A, B, ... E.
function A(x, y) % The Primary function
B(x,y)
D(y)
function B(x,y) % Nested in A
C(x)
D(y)
function C(x) % Nested in B
D(x)
end % This terminates C
end % This terminates B
function D(x) % Nested in A
E(x)
function E(x) % Nested in D
disp(x)
end % This terminates E
end % This terminates D
end % This terminates A
Every function has a certain scope, that is, a set of other functions to which it is visible. A nested function is available:
- From the level immediately above it. (In the previous code, function A can call B or D, but not C or E.)
- From a function nested at the same level within the same parent function. (Function B can call D, and D can call B.)
- From a function at any lower level. (Function C can call B or D, but not E.)
- If you construct a function handle for a nested function, you can call the nested function from any MATLAB function that has access to the handle.
Private Functions
Private Functions
Private functions reside in subfunctions with the special name private, and they are visible only to function in the parent directory.
Private functions are useful when you want to limit the scope of a function. You designate a function as private by storing it in a subfolder with the name private. Then, the function is available only to functions in the folder immediately above the private subfolder, or to scripts called by the functions that reside in the parent folder.
For example, within a folder that is on the MATLAB search path, create a subfolder named private. Do not add private to the path. Within the private folder, create a function in a file named findme.m:
function findme
% FINDME An example of a private function.
disp('You found the private function.')
end
Change to the folder that contains the private folder and create a file named visible.m.
function visible
findme
end
Change your current folder to any location and call the visible function.
>> visible
You found the private function.
Although you cannot call the private function from the command line or from functions outside the parent of the private folder, you can access its help:
>> help private/findme
findme An example of a private function.
Private functions have precedence over standard functions, so MATLAB finds a private function named test.m before a nonprivate program file named test.m. This allows you to create an alternate version of a particular function while retaining the original in another folder.
Practice Exercise 5.4
- Use a primary function that uses a subfunction to compute the zeros of the function \(3{{x}^{3}}-12{{x}^{2}}-33x+80\) over the range -10 ≤ x ≤ 10.
5.5 Function in a Script File
To create a script file, you can
- Click New Script icon
 .
. - or, click
 icon, then select
icon, then select  icon to create function.
icon to create function.
Another option for storing function is to include them at the end of a script file. For instance, create a file named mystates.m with a few commands and two functions, fact and perm. The script calculates the permutation of (3,2).
x = 3;
y = 2;
z = perm(x,y)
function p = perm(n,r)
p = fact(n) * fact(n-1);
end
function f = fact(n)
f = prod(1:n);
end
Call the script from the command line.
>> mystates
z = 6
5.6 Local and Global Variables
Local Variables
Local Variables
The variables used in function files are known as local variables. The only way a function can communicate with the workspace is through input parameters and the output it returns. Any variables defined within the function exist only for the function to use.
For example, create a function named g.m to multiply two variables together:
function output = g(x,y)
a = x .* y;
output = a;
end
The variables a, x, y and output are local variables. They can be used for additional calculations inside the g function, but they are not stored in the workspace.
Persistent Variables
Persistent Variables
When you declare a variable within a function as persistent, the variable retains its value from one function call to the next. Other local variables retain their value only during the current execution of a function. Persistent variables are equivalent to static variables in other programming languages.
Declare variables using the persistent keyword before you use them. MATLAB initializes persistent variables to an empty matrix, [].
Find the Sum Value
For example, define a function in a file named findSum.m that initializes a sum to 0, and then adds to the value on each iteration.
function findSum(inputvalue)
persistent SUM_X
if isempty(SUM_X)
SUM_X = 0;
end
SUM_X = SUM_X + inputvalue;
end
When you call the function, the value of SUM_X persists between subsequent executions.
Counter
Create a count function to display how many time the function called.
function Counter()
persistent Counter ; % this is the important line
if isempty(Counter)
Counter = 1; % initialize first time
else
Counter = Counter + 1; % increment other times
end
fprintf('Counter = %d\n', Counter)
end % function Counter
Global Variables
Global Variables
global var1 ... varN
Declares variables var1 ... varN as global in scope.
Ordinarily, each MATLAB function has its own local variables, which are separate from those of other functions and from those of the base workspace. However, if several functions all declare a particular variable name as global, then they all share a single copy of that variable. Any change of value to that variable, in any function, is visible to all the functions that declare it as global.
- If the global variable does not exist the first time you issue the global statement, it is initialized to an empty 0x0 matrix.
- A global variable must be declared global before it is used the first time in a function.
- Global variable declarations should be placed at the beginning of a function definition.
- If a variable with the same name as the global variable already exists in the current workspace, MATLAB issues a warning and changes the value of that variable and its scope to match the global variable.
However, global variables carry notable risks. For example:
- Any function can access and update a global variable. Other functions that use the variable might return unexpected results.
- If you unintentionally give a “new” global variable the same name as an existing global variable, one function can overwrite the values expected by another. This error is difficult to diagnose.
Create a Simple Global Variable
create a function in a file called falling.m:
function h = falling(t)
global GRAVITY
h = 1/2 * GRAVITY *t .^ 2;
end
Then, enter these commands at the prompt:
>> global GRAVITY
>> GRAVITY = 32;
>> y = falling((0:.1:5)');
- To clear a global variable from all workspaces, use clear global variable.
- To clear a global variable from the current workspace but not other workspaces, use clear variable.
Variable Scope and Lifetime
Variable Scope and Lifetime
Variable Scope
Variable scope refers to the extent of code in which a variable can be referenced (accessed and modified).
- Variables defined inside a function are called local variables:
The scope of local variables and dummy arguments is limited to the function in which they are defined. If the function contains nested functions, the code in the nested functions can access all variables defined in their "parent" function. - Variables stored in the MATLAB workspace (called global memory) are called global variables:
By default, the scope of global variables is the command line and all scripts. - Most of the time using global variables is a bad idea.
- Occasionally, it is useful to access global variables from within a function when the variables contain large amounts of data. There can be significant memory and time savings if the data is large.
Variable Lifetime
Variable lifetime refers to how long a variable remains in existence.
- The lifetime of a local variable is limited to the execution time of the function in which the variable is defined. When a function terminates, its local workspace ceases to exist (which includes all local variables and dummy argument variables).
- If a function gets called more than once, its local variables are "recreated" each time it is called.
- The lifetime of a global variable is indefinite -- the variable exists until it is explicitly cleared (with the clear global command) or until MATLAB terminates.
- The use of persistent variables extends the lifetime of local variables across multiple function calls.
- To make a local variable persistent, you must explicitly label the variable as persistent.
- While a persistent variable has an extended lifetime, it does not have an extended scope.
5.7 Recursive Functions
Recursive Functions
Functions can be recursive, that is, they can call themselves. Recursion is a powerful tool, but not all computations that are described
recursively are best programmed this way.
Calculate Factorial Using Recursive Function
Create a function file test.m to calculate \(n!\), n = 1 ~ 10.
function test
clc;
for k = 1 : 10
kFactorial = fact(k);
fprintf('%d! = %d\n', k, kFactorial);
end
function x = fact(n)
if (n <= 1)
x = 1;
else
x = n .* fact(n-1);
end
In the command window you'll see:
>> test
1! = 1
2! = 2
3! = 6
4! = 24
5! = 120
6! = 720
7! = 5040
8! = 40320
9! = 362880
10! = 3628800
Questions
- Perhaps the most famous equation in physics is
\(E=m{{c}^{2}}\)
which relates energy E to mass m. The speed of light in a vacuum, c, is the property that links the two together. The speed of light in a vacuum is \(2.9979\times {{10}^{8}}\) m/s.- Create a function called energy to find the energy corresponding to a given mass in kilograms. Your result will be in joules, since \(1\,kg{}^{{{m}^{2}}}\!\!\diagup\!\!{}_{{{s}^{2}}}\;=1\,J\).
- Use your function to find the energy corresponding to masses from 1 kg to 106 kg. Use the logspace function (consult help logspace) to create an appropriate mass vector.
- Create four anonymous functions to represent the function \(6{{e}^{3\cos {{x}^{2}}}}\), which is composed of the functions \(h(z)=6{{e}^{z}}\), \(g(y)=3\cos y\), and \(f(x)={{x}^{2}}\). Use the anonymous function to plot \(6{{e}^{3\cos {{x}^{2}}}}\) over the range 0 ≤ x ≤ 4.

